建造者模式是六个创建型模式中的一个,和工厂模式有相同点,也有区别。
工厂模式关心最终的产品,建造者模式还关心创建的细节,所以建造者模式常用来创建复杂的对象。
此次学习参考LoveLion的复杂对象的组装与创建——建造者模式(二),实例则使用C++重新实现
概述
建造者模式是较为复杂的创建型模式,它将客户端与包含多个组成部分(或部件)的复杂对象的创建过程分离,客户端无须知道复杂对象的内部组成部分与装配方式,只需要知道所需建造者的类型即可。它关注如何一步一步创建一个的复杂对象,不同的具体建造者定义了不同的创建过程,且具体建造者相互独立,增加新的建造者非常方便,无须修改已有代码,系统具有较好的扩展性。
建造者模式(Builder Pattern):将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。建造者模式是一种对象创建型模式。
类图如下:
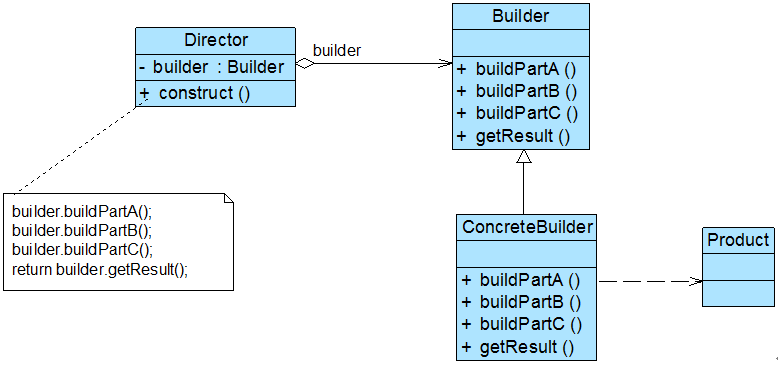
在建造者模式结构图中包含如下几个角色:
Builder(抽象建造者):它为创建一个产品Product对象的各个部件指定抽象接口,在该接口中一般声明两类方法,一类方法是buildPartX(),它们用于创建复杂对象的各个部件;另一类方法是getResult(),它们用于返回复杂对象。Builder既可以是抽象类,也可以是接口。
ConcreteBuilder(具体建造者):它实现了Builder接口,实现各个部件的具体构造和装配方法,定义并明确它所创建的复杂对象,也可以提供一个方法返回创建好的复杂产品对象。
Product(产品角色):它是被构建的复杂对象,包含多个组成部件,具体建造者创建该产品的内部表示并定义它的装配过程。
Director(指挥者):指挥者又称为导演类,它负责安排复杂对象的建造次序,指挥者与抽象建造者之间存在关联关系,可以在其construct()建造方法中调用建造者对象的部件构造与装配方法,完成复杂对象的建造。客户端一般只需要与指挥者进行交互,在客户端确定具体建造者的类型,并实例化具体建造者对象(也可以通过配置文件和反射机制),然后通过指挥者类的构造函数或者Setter方法将该对象传入指挥者类中。
实例
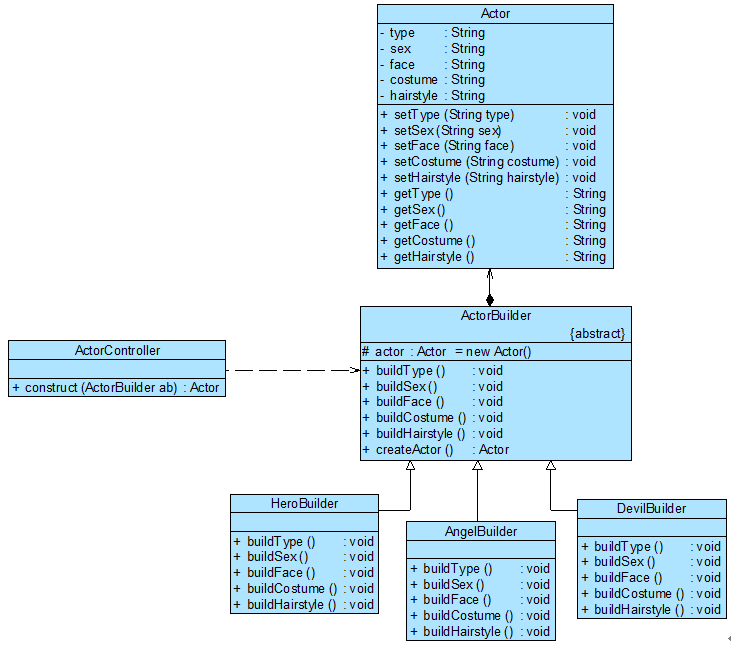
直接使用C++实现原文中的游戏角色创建,类图如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Actor
{
private:
string m_type;
string m_sex;
string m_face;
string m_costume;
string m_hairstyle;
public:
Actor()
{
m_type = "";
m_sex = "";
m_face = "";
m_costume = "";
m_hairstyle = "";
}
void setType(string type)
{
m_type = type;
}
void setSex(string sex)
{
m_sex = sex;
}
void setFace(string face)
{
m_face = face;
}
void setCostume(string costume)
{
m_costume = costume;
}
void setHairstyle(string hairstyle)
{
m_hairstyle = hairstyle;
}
string getType()
{
return m_type;
}
string getSex()
{
return m_sex;
}
string getFace()
{
return m_face;
}
string getCostume()
{
return m_costume;
}
string getHairstyle()
{
return m_hairstyle;
}
};
class ActorBuilder
{
protected:
Actor actor;
public:
ActorBuilder() {}
virtual void buildType() = 0;
virtual void buildSex() = 0;
virtual void buildFace() = 0;
virtual void buildCostume() = 0;
virtual void buildHairstyle() = 0;
Actor createActor()
{
return actor;
}
};
class HeroBuilder : public ActorBuilder
{
public:
HeroBuilder() {}
void buildType()
{
actor.setType("英雄");
}
void buildSex()
{
actor.setSex("男");
}
void buildFace()
{
actor.setFace("英俊");
}
void buildCostume()
{
actor.setCostume("盔甲");
}
void buildHairstyle()
{
actor.setHairstyle("飘逸");
}
};
class AngelBuilder : public ActorBuilder
{
public:
AngelBuilder() {}
void buildType()
{
actor.setType("天使");
}
void buildSex()
{
actor.setSex("女");
}
void buildFace()
{
actor.setFace("漂亮");
}
void buildCostume()
{
actor.setCostume("白裙");
}
void buildHairstyle()
{
actor.setHairstyle("披肩长发");
}
};
class DevilBuilder : public ActorBuilder
{
public:
DevilBuilder() {}
void buildType()
{
actor.setType("恶魔");
}
void buildSex()
{
actor.setSex("妖");
}
void buildFace()
{
actor.setFace("丑陋");
}
void buildCostume()
{
actor.setCostume("黑衣");
}
void buildHairstyle()
{
actor.setHairstyle("光头");
}
};
class ActorController
{
public:
ActorController(){}
Actor construct(ActorBuilder *ab)
{
Actor actor;
ab->buildType();
ab->buildSex();
ab->buildFace();
ab->buildCostume();
ab->buildHairstyle();
actor = ab->createActor();
return actor;
}
};
int main ()
{
ActorBuilder *ab = new DevilBuilder();
ActorController ac;
Actor actor;
actor = ac.construct(ab);
cout << actor.getType() << "的外观:" << endl;
cout << "性别:" << actor.getSex() << endl;
cout << "面容:" << actor.getFace() << endl;
cout << "服装:" << actor.getCostume() << endl;
cout << "发型:" << actor.getHairstyle() <<endl;
return 0;
}
|

